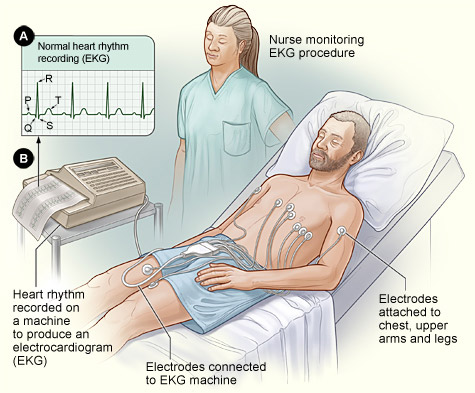
What is the difference between an Electrocardiogram (ECG) and an Echocardiogram (Echo)?
(a) An Electrocardiogram (ECG) is a recording of the heart’s electrical activity.
(b) An Echocardiogram (Echo) is an ultrasound image of the heart in motion.
How is the Electrocardiogram (ECG) performed?
The nurse or technician attaches electrodes that transmit electrical activity from the patient to the ECG machine. The electrical activity is recorded by the ECG machine, printed out and then interpreted by a physician or cardiologist.
What are some common indications for an Electrocardiogram (ECG)?
- To assess the heart rhythm and heart rate.
- To determine whether chest pain is due to angina or a heart attack- otherwise known as ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI).
- To assess abnormal cardiac structure such as enlargement or hypertrophy of the cardiac chambers.
- To determine whether there is inflammation of the covering of the heart (pericarditis).