What is an Echo?
Echocardiography (Echo) utilizes ultrasound imaging and doppler physiology, to evaluate the structure and function of your heart.
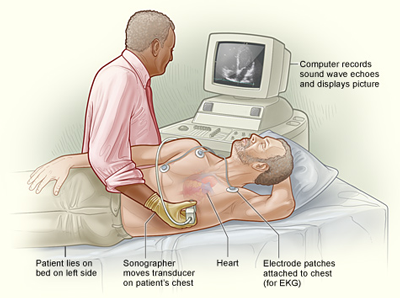
What is a Trans-thoracic Echo (TTE)?
During a trans-thoracic echo, a sensor (transducer) is applied to your chest wall. The sensor sends and receives sound waves that produce two-dimensional (2D) images of your moving heart and doppler recordings of the flow of blood through your heart. The processed images are recorded digitally and then interpreted by your Cardiologist.
What are some common indications for a Trans-thoracic Echo (TTE)?
- To assess the contractile function of your heart by calculating the left ventricular ejection fraction. The ejection fraction is normally greater than 60%.
- To determine the underlying cause of heart failure and assess its severity.
- To detect complications of coronary artery disease such as muscle damage, impaired systolic (contractile) function and heart failure following a heart attack.
- To assess valvular heart disease, its causes and severity.
- To detect cardiac complications of hypertension (high blood pressure) such as: hypertrophy (thickened heart muscle), enlargement, impaired systolic (contractile) function, impaired diastolic (relaxing) function and heart failure.
Echo: Normal left ventricular function
This echo (short-axis view) demonstrates normal contractility of all left ventricular segments. The ejection fraction is 65%.