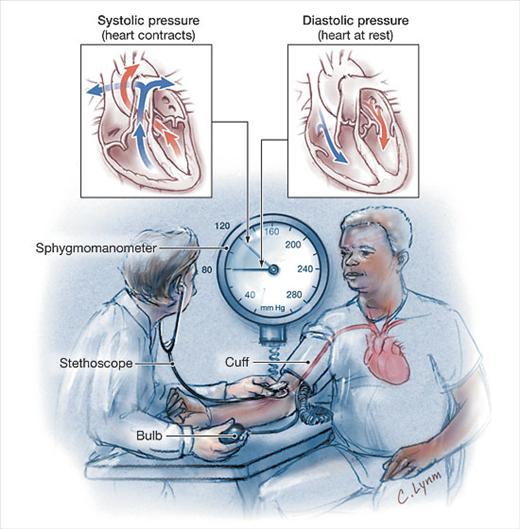
What is the normal Blood Pressure?
Blood Pressure (BP) is a measure of the force the circulating blood exerts on the artery wall. BP is measured with a sphygmomanometer. The normal systolic BP of an adult is less than 120mmHg and the normal diastolic BP is less than 80 mmHg (Normal BP<120/80 mmHg).
How is Hypertension classified?
Here is a simplified definition and classification of normal and abnormal blood pressure.
| Blood Pressure (BP) | Classification |
| <120/80 mmHg | Normal BP |
| >120/80 mmHg | Elevated BP |
| >130/80 mmHg | Stage I Hypertension (Pre-Hypertension) |
| >140/90 mmHg | Stage II Hypertension |
Fig 2: Normal and abnormal BP
![]()
Essential hypertension means there is no underlying cause of the hypertension. Secondary hypertension (5% of cases) is due to an underlying problem such as kidney or adrenal disease.
What are the symptoms and complications of hypertension?
Hypertension does not cause symptoms unless complications occur. The elevated BP puts a strain on the arteries, the heart and the kidneys. If left untreated, it leads to complications (heart attack, stroke, atrial fibrillation, heart failure, renal failure).
How is hypertension treated?
There is no permanent cure but hypertension can be treated by lifestyle changes and medication. There are four lifestyle changes that may help lower BP. They are exercise, weight loss, reduction of salt intake and limiting alcohol consumption.
In some patents, lifestyle changes alone are not enough to lower blood pressure to acceptable levels. These patients require medication in addition to healthy lifestyle changes.
What medications are used to treat hypertension?
Current guidelines recommend using medications from one or more of the following three groups as the principal drugs for the treatment of hypertension.
- Diuretics increase the excretion of salt and water in the urine.
- Calcium Channel Blockers are direct vasodilators that relax the arteries.
- ACE Inhibitors and ARBs block salt retention and arterial vasoconstriction.
Additional drugs that may be used include aldosterone-blockers, alpha receptor-blockers, beta-blockers, vasodilators and central agents
What are the goals of treatment?
For most patients, the BP should be reduced to less than 130/80mmHg. Treatment can be monitored by office BP, home BP or ambulatory BP measurement. Studies have shown that when hypertension has been treated effectively, patients have fewer complications and live longer.