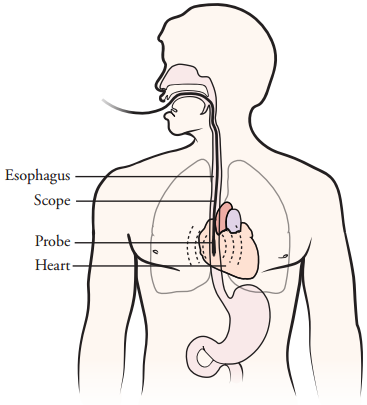
TEE: A transducer placed in the esophagus behind the heart acquires images of the heart
What is a Trans-esophageal Echo (TEE)?
TEE is a specialized echo exam that lets your doctor see images of your heart from a small sensor (transducer) on the tip of a thin tube that is placed in the esophagus (swallowing tube) behind the heart. The sensor sends and receives sound waves that produce high quality images of the heart. A cardiologist trained to do this exam will perform your test. A mild sedative may be given to you. You’ll lie on your side for the tube to be inserted whilst the images of your heart are recorded. After the test, the tube will be gently removed.
What is a Trans-esophageal Echo (TEE) used for?
TEE will provide clearer or more detailed images of the heart if the TTE images are not clear enough. It may be useful to evaluate:
- Congenital heart disease. These are cardiac defects that were present at birth
- Aortic dissection. This is a tear in the wall of the aorta.
- Aneurysms of the aorta or left ventricle.
- Valvular heart disease.
- Infective endocarditis. This is an infection of the heart, usually affecting the heart valves.
- Cardiac tumors
- Thromboembolism and Stroke. Blood clots can form inside the heart chambers, break free, and then flow to the brain or other areas of the body. This can cause a stroke or other problems. Most often these clots form with irregular heart rhythms or stagnant blood flow in the heart.
What is Trans-esophageal Echo (TEE) Cardioversion?
TEE may be done in patients with atrial fibrillation/ flutter to make sure no clots are present in the left atrium prior to cardioversion.


